Table of Contents
Truthfully Labelled Seed Definition
A Truthful Label is an official tag found on seed packets that provides detailed, essential information about the seeds inside. A truthful label is like a guarantee from the seed company to the buyer that the seeds meet certain quality standards.
A truthful Label is a mandatory requirement where the seed producer or seller must clearly state essential details, such as Variety of the seeds, Purity percentage, Germination rate, and Other vital information.
The main purpose of the Truthful Label is to ensure that farmers receive accurate, reliable information about the seeds they are purchasing, even if the seeds have not been officially certified. This transparency allows farmers to make informed choices that can significantly impact their crop yield and quality.
But how did the concept of the Truthful Label come about? Let’s explore its origin and understand its significance.
The Origin of the Truthful Label
The Truthful Label was introduced to protect farmers by ensuring that only high-quality seeds are sold. To achieve this, the government enacted the Seed Act of 1966 and the Seed Rules of 1968. These regulations mandated that all seeds sold in the country must have a Truthful Label.
This requirement was established to provide farmers with clear and accurate information about the seeds they purchase, preventing them from falling prey to low-quality or misleading products. The Truthful Label, therefore, plays a crucial role in helping farmers choose the best seeds for their fields, ultimately leading to better crop yields and sustainable farming practices.

How Do Seed Producers and Sellers Obtain a Truthful Label?
To obtain a Truthful label, seed producers and sellers must follow a specific process to ensure that their seeds meet the quality standards set by the government.
Here’s a breakdown of how this is done:
Conducting Quality Tests:
The seed producer must carry out various tests to assess the quality of the seeds. These tests typically include Germination Test, Physical Purity Test, Moisture Test, Genetic Purity Test and Other Relevant Tests.
These tests can be performed either in-house or outsourced to an accredited external agency. All tests must meet the standards set by the Indian government for the specific type of seeds being sold.
Documentation of Test Results:
Once the tests are completed, the results must be thoroughly documented. This documentation includes Detailed records of test outcomes (e.g., germination percentage, purity levels), Date of testing, Batch numbers, and Any other relevant information
Preparing the Truthful Label:
Based on the test results, a Truthful Label is created that includes all the required information in a format that complies with the specifications outlined in the Seed Rules. The label must accurately reflect the seed quality data from the tests.
Submission to the State Agricultural Department:
The prepared Truthful Label, along with other necessary details and documents, is submitted to the state agricultural department. The department may inspect the seed batches to ensure compliance with the Seed Act of 1966 and the Seed Rules of 1968.
Approval of the Truthful Label:
If the state agricultural department is satisfied that the seeds meet all the required standards, then the Truthful Labe will be approved. This approval might be communicated through an official certificate or a formal communication. (Please note that this approval process can vary based on the state and its specific guidelines.)
Printing and Affixing the Label:
After receiving approval, the Truthful Labels are printed according to the approved format. These labels are then securely affixed to seed packets to ensure they remain intact during handling, transportation, and storage.
Difference Between Truthfully Labelled Seeds and Certified Seeds
| Truthfully Labeled Seed | Certified Seed | |
| Definition | Seeds labeled by the producer with key information, but without official government certification. | Seeds that have been certified by a government or authorized body after passing strict quality checks. |
| Certification Authority | No formal certification authority is involved—reliant on producer’s labeling. | Certified by government or authorized agencies like the State Seed Certification Agency (SSCA). |
| Tag Color | Opal green tag. | Blue tag. |
| Standards | Follows general guidelines, but less rigorous compared to certified seeds. | Must meet strict standards for purity, quality, and germination rate. |
| Cost | Generally more affordable since it doesn’t go through official certification. | Typically more expensive due to extensive testing and certification. |
Components of a Truthful Label
A Truthful Label is opal green in color and measures 15 cm x 10 cm.
It contains the following components:
- Kind
- Variety
- Lot Number
- Label Number
- Date of Test
- Date of Packing
- Valid Upto Date
- Pure Seed Percentage (%)
- Inert Matter Percentage (%), Other Crop Seed Percentage (%), Weed Seed Percentage (%)
- Germination Percentage (%)
- Genetic Purity percentage (%)
- Net Content
- Chemical Treatment Information (if applicable)
- MRP
- Unit Sale Price
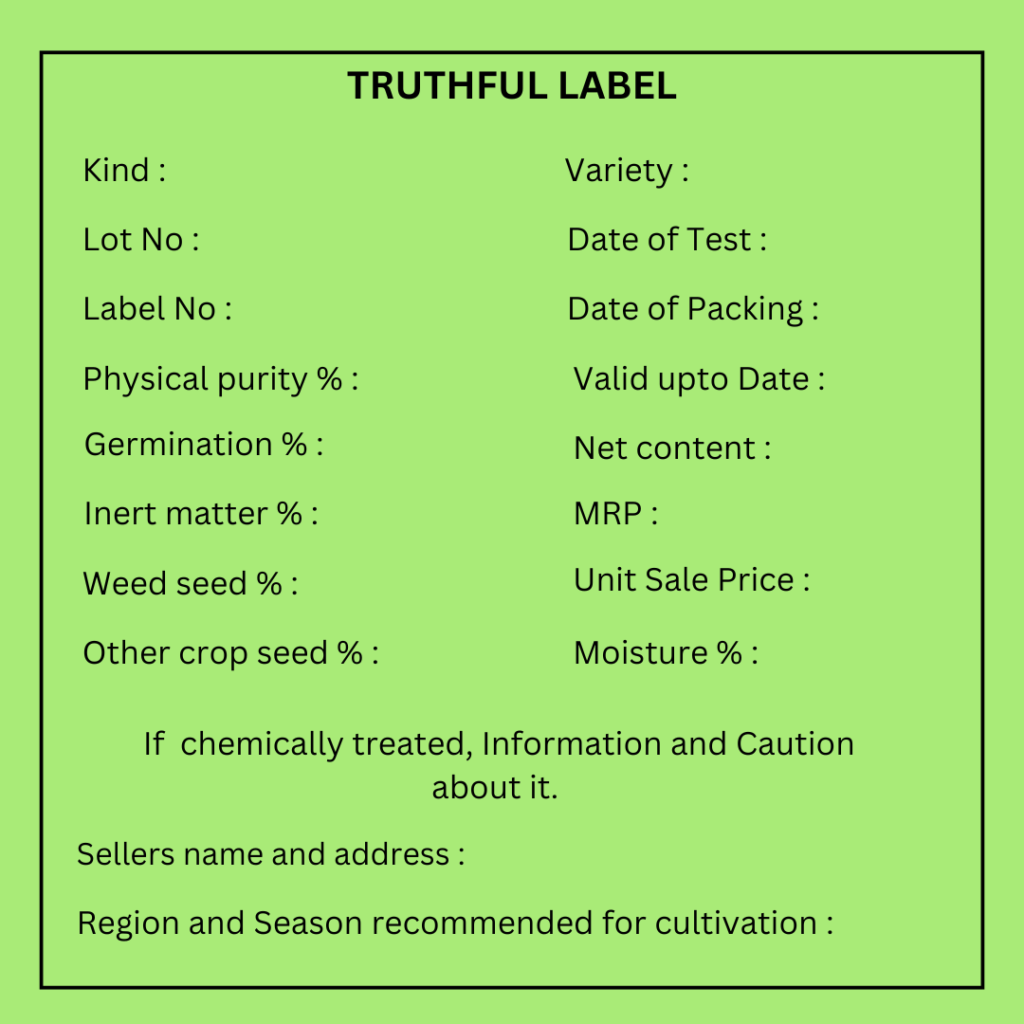
The meaning and importance of each of the above components are mentioned below.
1. Kind
“Kind” refers to the general type or category of the crop seed, such as Hybrid Chilli.
Farmers must check the “Kind” to ensure they are purchasing the correct seed for their specific farming needs. Miscommunication about seed type can lead to planting the wrong crops, which may not be suited to the soil, climate, or intended market. Confirming the “Kind” ensures they choose the right plant for optimal growth and yield.
2. Variety
“Variety” specifies the particular breed or cultivar of the seed. Even within the same “Kind,” there can be multiple cultivars with varying traits.
Different varieties perform better in specific climates, soil conditions, and yield requirements. By checking the “Variety,” farmers can select the most suitable option for their region, improving the chances of better crop performance and higher profitability.
3. Lot Number
A “Lot Number” is a unique identification number assigned to a specific batch of seeds created during manufacturing or packaging.
Importance of Lot Number for Farmers:
- Traceability and Addressing Issues:
Lot numbers allow farmers to trace the origin of their seeds, which is essential if they face issues such as poor germination or contamination. By referencing the lot number, they can directly report problems to the supplier or manufacturer, making it easier to resolve complaints and seek replacements or refunds.
- Recall Management:
In the event of quality issues with a particular batch, the lot number enables targeted recalls, ensuring that only the affected seeds are removed from the market. This minimizes disruption and ensures that unaffected seeds remain available to farmers.
- Ensuring Consistency:
Farmers can check the lot number to confirm they are planting seeds from a consistent batch. This is crucial for achieving uniform crop growth, especially in large-scale operations, where consistency in quality directly impacts yield.
- Managing Planting and Harvesting:
By keeping track of lot numbers, farmers can better manage planting schedules and evaluate the performance of different seed batches. This helps in making informed decisions for future seed purchases and harvest planning.
4. Label Number
A Label Number is a unique identification number assigned to each seed packet, ensuring traceability and verification of the packet’s information.
The Label Number helps farmers confirm that the seeds are genuine and not counterfeit. Authentic seed packets display all necessary information, and the Label Number can be cross-referenced with records from the seed producer or regulatory authorities. In the event of quality issues or recalls, the Label Number allows farmers to trace the specific batch of seeds they have purchased, helping identify the affected batch and take appropriate actions, such as seeking replacements or refunds.
5. Date of Test
The “Date of Test” indicates when the seeds were last tested for quality parameters such as germination rate, purity, and overall seed health.
This date gives farmers a clear indication of how recently the seed quality has been verified. Seeds tested recently are likely to have accurate quality data, giving farmers confidence in the seed’s performance and viability.
6. Date of Packing
The “Date of Packing” indicates the exact date when the seeds were packaged for sale.
Seeds lose viability over time. Research shows that seed viability can decline by 10-30% annually, depending on storage conditions. Properly packed and stored seeds maintain higher germination rates (source: Journal of Agricultural Science). Freshly packed seeds generally have higher germination rates and better seed health, ensuring successful crop establishment.
7. Valid Upto Date
The “Valid Upto Date” specifies the last date until which the seed’s quality is guaranteed, particularly its germination rate.
After this date, the seed’s performance may decline, with lower germination rates and weaker crop establishment. Farmers should always check this date to ensure they are planting viable seeds and minimizing the risk of poor crop growth. Using seeds past this date can lead to suboptimal results, including reduced yields and wasted resources.
8. Pure Seed %
The “Pure Seed %” is the percentage of seeds in the package that are of the specified crop, free from contaminants like weed seeds, other crop seeds and inert matter.
The “Pure Seed %” is an important indicator of seed quality. A higher percentage means that the majority of the package consists of viable seeds of the desired crop, ensuring that farmers are getting what they paid for. A low pure seed percentage indicates the presence of contaminants or inert matter, which can negatively affect planting and crop performance. By choosing seeds with a high purity percentage, farmers can ensure a higher number of healthy plants per hectare, leading to better yields and overall profitability.
9. Inert Matter %, Other Crop Seed %, and Weed Seed %
Inert Matter % refers to non-seed material like soil, stones, or broken seed parts.
Other Crop Seed % shows the percentage of seeds from other crops mixed in.
Weed Seed % indicates the presence of weed seeds in the seed lot.
High percentages of inert matter, other crop seeds, and weed seeds reduce the overall quality of the seed lot. Inert matter doesn’t contribute to crop growth, and other crop or weed seeds can lower the purity and quality of the crop. Additionally, weed seeds can grow into unwanted plants, competing with the main crop for nutrients, water, and sunlight. This forces farmers to invest additional resources in removing weeds or using herbicides, both of which increase costs and labour.
By choosing seeds with lower percentages of inert matter, other crop seeds, and weed seeds, farmers can ensure higher purity and better crop outcomes, reducing waste and improving profitability.
10. Germination %
The “Germination %” refers to the percentage of seeds expected to sprout and grow into seedlings under ideal conditions. For example, a germination rate of 90% means that 90 out of 100 seeds are likely to germinate.
This percentage is critical for farmers as it directly impacts crop establishment and yield. A higher germination rate ensures more plants will grow, leading to a uniform crop and better productivity. It also helps farmers calculate the optimal seeding rate, ensuring efficient use of seeds, water, and fertilizers. Seeds with low germination percentages can lead to uneven growth, poor yields, and higher costs due to the need for replanting.
11. Genetic Purity %
Genetic Purity Percentage refers to how genetically true-to-type the seeds are compared to the parent variety. It ensures that the seeds carry the specific traits of the Variety, such as disease resistance or growth characteristics.
Importance of Genetic Purity Percentage for Farmers:
- Uniformity: High genetic purity guarantees uniform crop growth, with all plants displaying consistent characteristics. This simplifies crop management and ensures uniformity at harvest time.
- Trait Reliability: Farmers relying on specific traits like drought tolerance or pest resistance benefit from high genetic purity, which ensures these traits will be present. Low genetic purity may lead to inconsistent traits, negatively impacting crop performance and profitability.
- Market Value: Crops grown from genetically pure seeds are more likely to be uniform in quality, size, and appearance, which can result in higher market prices.
12. Net Content
“Net Content” refers to the total weight or quantity of seeds in the packet, usually expressed in grams, kilograms, or the number of seeds.
This information ensures farmers know exactly how much seed they are purchasing and planting. It also ensures consistency and reliability in seed purchases, which is important for large-scale farming operations. It protects them from fraud or misrepresentation, ensuring they receive the promised amount of seeds. It also protects farmers from Overpricing frauds. Ex – Selling a Less no. of seeds at a higher price.
13. Chemical Treatment Information
If seeds have been chemically treated with pesticides, fungicides, or other coatings, this must be clearly indicated on the seed label.
Importance to Farmers :
- Safe Handling: Farmers can take necessary precautions, like wearing gloves or masks, to protect themselves and their workers from exposure to harmful substances.
- Avoiding Overuse of Chemicals: Knowing the seeds are already treated helps farmers avoid unnecessary chemical applications, reduce costs, and prevent over-treatment, which could harm the soil or crops.
- Consumer Awareness: For farmers growing organic or chemical-free crops, this label ensures they can avoid treated seeds, maintaining the integrity of their produce and meeting market demand for chemical-free options.
14. MRP (Maximum Retail Price)
The Maximum Retail Price (MRP) is the highest price a retailer is allowed to charge for a packet of seeds. This price is legally mandated and printed on the seed packet.
MRP protects farmers from being overcharged by retailers. It ensures they pay a fair and transparent price. Additionally, knowing the MRP helps farmers plan their spending, allowing them to compare brands and varieties without exceeding their budget.
15. Unit Sale Price
The Unit Sale Price refers to the price per unit of seed, typically by weight or volume (e.g., price per kilogram).
Understanding the unit sale price ensures that farmers get the correct amount of seeds for the price they’re paying, preventing overcharging. When buying in bulk, comparing unit sale prices across brands helps farmers make informed decisions, ensuring they get the best value for their money while meeting their crop needs.
Other Components that can be checked on a seed Packet are
1. Moisture %
The “Moisture %” refers to the percentage of water present in the seeds at the time of packaging.
Significance:
- Seed Longevity and Storage: Moisture content is critical for seed storage life. Seeds with high moisture are more prone to spoilage, fungal growth, or insect damage. A lower moisture percentage extends the shelf life of seeds, ensuring they remain viable for the next planting season. This allows farmers to store seeds with confidence, reducing the risk of deterioration.
- Germination Success: The moisture level also affects germination rates. If seeds contain too much moisture, they may sprout prematurely during storage, making them ineffective when planted. On the other hand, very low moisture can reduce germination capability. Checking the moisture percentage ensures that the seeds are in the best condition for planting and successful crop establishment.
2. Seller’s Name and Address (Produced, Packed and Marketed by)
The “Seller’s Name and Address” provides the legal name and physical location of the seller responsible for supplying the seeds.
This information allows farmers to trace the source of their seeds and resolve any issues, such as poor germination or contamination. It ensures transparency, accountability, and legal protection in case of fraud or misrepresentation. A reliable seller’s information also helps farmers build trust and long-term relationships for consistent access to high-quality seeds, along with personalized advice and better deals.
3. Region and Season Recommended for Cultivation
This indicates the ideal geographical regions and time periods for planting the seeds based on climate, soil conditions, and crop-growing patterns.
Significance:
- Optimized Crop Performance: Planting in the wrong season or region can expose crops to adverse weather, diseases, or pests, leading to poor yields or crop failure. By checking the recommended region and season, farmers can align their planting schedules with favourable conditions, reducing the risk of loss and ensuring a successful harvest.
- Tailored Planning: This information helps farmers choose seeds suited to their local climate, soil type, and typical weather patterns. It also assists with crop rotation planning and resource management, ensuring that planting strategies are aligned with local market demands, thereby improving profitability.
Importance of Checking the Seed Packet for Farmers
1. Avoiding Counterfeit Products:
By carefully examining the seed packet, farmers can ensure they are not falling victim to counterfeit products. Authentic seed packets display all required information and certifications, allowing farmers to verify the legitimacy of the seeds.
This prevents the purchase of substandard seeds that could lead to poor crop performance and financial losses. Ensuring that seeds are genuine helps maintain the integrity of the farming operation and protects against deceptive practices in the market.
2. Accessing Detailed Information for Better Yields:
Seed packets provide comprehensive details about the seed’s genetic purity, germination percentage, moisture content, and recommended planting conditions. This information is crucial for understanding the quality and suitability of the seeds.
With accurate and detailed information, farmers can make informed decisions about which seeds to plant, optimizing their crop management practices. This leads to better yields and enhances overall productivity, as farmers can select seeds that align with their specific farming conditions and goals.
3. Selecting Better Quality Seeds for Specific Needs:
The seed packet includes information on the ideal region and season for sowing, as well as other key factors, such as whether the seeds have been treated with chemicals. This helps farmers choose seeds that are tailored to their specific field conditions and requirements.
Farmers can purchase seeds that are best suited for their local climate and soil, which increases the likelihood of successful crop growth and high yields. By selecting seeds that meet their precise needs, farmers can improve their crop quality, manage resources more effectively, and achieve better economic returns.
In summary, paying attention to the details on seed packets can make a significant difference in the success of your crops. By understanding and utilizing the information provided—such as germination rates, moisture content, and optimal planting conditions—you can ensure healthier plants and better yields.

Join DesiKheti Whatsapp Channel for regular updates, farming tips, and information on agriculture.
